by Julia Layton and Karim Nice
Gasoline-electric hybrid cars contain the following parts:
Gasoline engine - The hybrid car has a gasoline engine much like the one you will find on most cars. However, the engine on a hybrid is smaller and uses advanced technologies to reduce emissions and increase efficiency.
Gasoline engine - The hybrid car has a gasoline engine much like the one you will find on most cars. However, the engine on a hybrid is smaller and uses advanced technologies to reduce emissions and increase efficiency.
Fuel tank - The fuel tank in a hybrid is the energy storage device for the gasoline engine. Gasoline has a much higher energy density than batteries do. For example, it takes about 1,000 pounds of batteries to store as much energy as 1 gallon (7 pounds) of gasoline.
Electric motor - The electric motor on a hybrid car is very sophisticated. Advanced electronics allow it to act as a motor as well as a generator. For example, when it needs to, it can draw energy from the batteries to accelerate the car. But acting as a generator, it can slow the car down and return energy to the batteries.
Generator - The generator is similar to an electric motor, but it acts only to produce electrical power. It is used mostly on series hybrids (see below).
Batteries - The batteries in a hybrid car are the energy storage device for the electric motor. Unlike the gasoline in the fuel tank, which can only power the gasoline engine, the electric motor on a hybrid car can put energy into the batteries as well as draw energy from them.
Transmission - The transmission on a hybrid car performs the same basic function as the transmission on a conventional car. Some hybrids, like the Honda Insight, have conventional transmissions. Others, like the Toyota Prius, have radically different ones, which we'll talk about later.
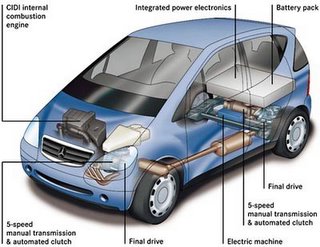
(Picture Right: The Mercedes-Benz M-Class HyPer -- a hybrid concept vehicle, Image courtesy DaimlerChrysler)
You can combine the two power sources found in a hybrid car in different ways. One way, known as a parallel hybrid, has a fuel tank that supplies gasoline to the engine and a set of batteries that supplies power to the electric motor. Both the engine and the electric motor can turn the transmission at the same time, and the transmission then turns the wheels.
You'll notice that the fuel tank and gas engine connect to the transmission. The batteries and electric motor also connect to the transmission independently. As a result, in a parallel hybrid, both the electric motor and the gas engine can provide propulsion power.
Typical Parallel Hybrid
4-cylinder Engine, Simillar to the engine in most cars, but smaller and more efficient.
Electric Motor, Simillar to the motor in electric car, but usually smaller since it doesn't have to power the by itself.
Transmission, Some hybrids have conventional transmissions, others use more exotic technology like CVTs.
Batteries, The batteries store energy recovered from braking or generated by the motor.
Fuel Tank, The main energy storage device for the hybrid, usually gives the car a range of 500 miles or more.
Typical Series Hybrid
By contrast, in a series hybrid (below), the gasoline engine turns a generator, and the generator can either charge the batteries or power an electric motor that drives the transmission. Thus, the gasoline engine never directly powers the vehicle.
Take a look at the explanation below of the series hybrid, starting with the fuel tank, and you'll see that all of the components form a line that eventually connects with the transmission.
Fuel Tank, The main energy storage device for the hybrid, the fual tank usually gives the car a range of 500 miles or more.
Electric Motor, Simillar to the motor on an electric car, the motor on a series hybrid provides all of the propultion power.
Transmission, Simillar to the transmission on electric vehicle, the motor can spin fast enough so that the transmission only needs one generator.
Batteries, The batteries store energy recovered from braking or generated by the motor.
Generator, This is where the gas engine's power gets converted to electrical power to drive the motor or charge the batteries.
Four-cylinder Engine, The engine on a series hybrid turns the generator. It is not able to power the car directly.
The structure of a hybrid car harnesses two sources of power to increase efficiency and provide the kind of performance most of us are looking for in a vehicle.
No comments:
Post a Comment